- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about CQ10
Photo credit: bigstock.com
You have probably seen CQ10 supplements in the vitamin aisle of your health food store and wondered exactly what it was. Well, keep reading to find out what CQ10 is, what it does, and why you need it.
Because it plays an important part in the human body, CQ10 is a popular supplement. This enzyme is absolutely necessary for the proper functioning of the body’s cells. OK, let’s get to everyone’s questions.
What exactly is CQ10?
Its complete name is coenzyme Q10, and this is an enzyme that is naturally found in the cells of our body. It’s found in the mitochondria, the rod shaped assembly inside every single cell that works something like a power generator for cells.
What does CQ10 do?
CQ10’s big job is in its role in the creation of a molecule that is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP for short. ATP directs energy where it is needed within the body. Therefore, ATP is essential for our metabolism. ATP is vital for most of the processes in the body, such as the contraction of muscles, including the heart. It’s also thought to function something like an antioxidant like selenium, and Vitamins E and C. Some scientists believe that there might be diseases that respond to supplementation of CQ10.
Take a look at some of the health benefits that doctors think taking CQ10 could help us with:
- Slow down the progression of dementia
- Treat or prevent migraines
- Increase sperm count
- Treat high blood pressure
- Stop heart disease
- Reduce cholesterol levels in the blood
- Providing energy for those suffering from fatigue
- Improve the immune system
- Treat gum disease
- Stabilize blood sugar levels
- Help in the treatment of cancer
Continue to Page 2

Photo credit: bigstock.com
How much CQ10 do I need?
Your body naturally produces CQ10. It always makes enough so that you never have a deficiency, so that means there are no known symptoms related to a deficiency. About 25 percent of the CQ10 in the bloodstream comes from dietary sources, the rest our bodies make for themselves.
SEE ALSO: This One Vitamin is Crucial for Your Heart
What are the main food sources of CQ10?
Dietary sources of CQ10 are rather limited, with chicken and beef being the major sources. It is also found in olive and grape seed oils, peanuts, sesame seeds, pistachios, and some fruits and vegetables including berries, oranges, apples, cauliflower, broccoli, and spinach.
You can buy supplements in several forms, including soft gel caps, tablets, and oral sprays. It’s recommended that adults take somewhere between 30 and 200 mgs per day. Children should not take this supplement.
Continue to Page 3
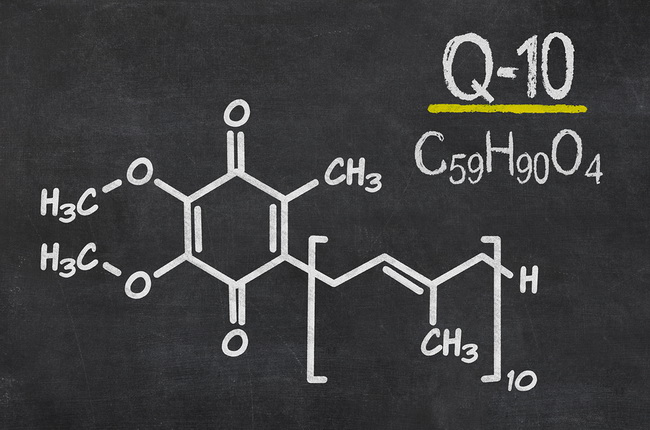
Photo credit: bigstock.com
What have research studies shown about CQ10?
One group of researchers studied how CQ10 affected patients with heart failure. They found that for subjects who took 100mg of CQ10 three times per day (for a total of 300mg daily), their hearts responded very positively. This study was done at The Heart Center at Copenhagen University Hospital in Denmark.
This study was a randomized controlled test that involved 420 subjects who had moderate to severe heart failure. The study followed these subjects over a two year period. Half of the subjects received a placebo, the other half consumed CQ10 three times per day.
At the end of this study, those who died in the CQ10 group were significantly lower than the placebo group (18 deaths versus 36 deaths).
Another study, performed by Karl Folkers, Ph.D., found that those with low blood levels of CQ10 were found in patients with heart disease and that 70 percent of his heart patients with congestive heart failure benefited greatly from taking CQ10 supplements.
Also, giving CQ10 supplements before heart surgery might reduce further damage caused by oxidative stress and free radicals, as well as strengthening heart function during recovery.
Some scientists believe that this shows that CQ10 is the first medication to improve survival rates for those with heart failure since beta blockers and ACE inhibitors were introduced more than 10 years ago. They believe that CQ10 should be added to current heart therapies.
Other doctors are not as confident. They point out that this is a small study and that more studies should be done before charging ahead with CQ10 therapy.
Another clinical trial showed that CQ10 supplements can help stop the heart damage that is often caused by the chemotherapy drug Adriamycin. Some very small studies showed that CQ10 shrank the tumors in women with breast cancer.
CQ10 has also been shown to control high blood pressure, but further studies need to be done.
Since many studies show that CQ10 can have positive effects on the blood, heart, and tissue toxicity, that this might mean that someday in the near future CQ10 can be used as part of a successful treatment program for recovery from stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and breast cancer treatment.
Continue to Page 4

Photo credit: bigstock.com
How does CQ10 do all this?
Although researchers aren’t exactly sure, they believe it might have something to do with CQ10’s ability to inhibit the formation of blood clots, act as a powerful antioxidant, and improve the production of energy within cells.
CQ10 can neutralize free radicals and reduce or stop some of the damage they cause. When combined with another powerful antioxidant, vitamin E, they help each other act more effectively in the body.
Even though scientists and doctors don’t know everything about CQ10 works, it’s fairly obvious that it’s a powerful supplement that has serious potential for curing many of our ills.
Sources:





























