- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
14 Types Of Headaches And How To Make Them Go Away!
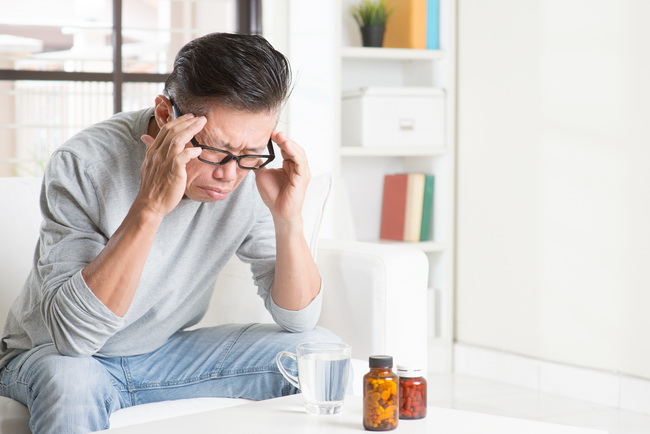

Photo credit: bigstock.com
7. The Sinus Headache
This type of headache should get a gold medal for being both misdiagnosed and over-diagnosed. Many doctors confuse migraines with sinus headaches. In fact, one study found that more than 87 percent of people with “sinus headaches” were actually suffering from migraines. The most common symptoms, such as watery eyes, sinus pressure, and nasal congestion, can happen with both sinus headaches and migraines. A true sinus headache is related to an infection. These types of headaches can be resolved over time. A migraine will make you sensitive to light, sound, and cause nausea.
8. The Cluster Headache
Not truly headaches, but most people believe that they are. The pain of a cluster headache is so intense that many people refer to them as suicide headaches, because some people have actually committed suicide rather than deal with another one. Cluster headaches generally happen at night, soon after a person falls asleep. They experience an excruciating pain on one side of the head, near the ear, with the pain radiating outwards across the face and under the jaw. Episodes can last from 15 minutes to three hours, and over-the-counter pain medications do nothing to stop the pain. This “headache” is actually caused by a swelling of the blood vessel that is right next to the joint of the jaw and ear. When it swells, it touches a nerve, causing intense pain. Doctors do not know the cause of this, but many people believe it is related to stress. Taking a steroid at the first sign of a cluster headache, such as prednisone, over a 10-day period seems to stop them but they can reoccur. See a doctor if you believe you are experiencing cluster headaches.
9. The Brain Tumor Headache
Yes, brain tumors generally cause people headaches but relax — these are the most uncommon types of headaches. Consider other options before you jump on this one.
10. The Migraine Headache
Although migraines are not completely understood, one thing doctors do know is that certain things trigger migraines. Some of them are out of your control, such as hormonal changes or stress, but some triggers are within your control, such as sleeping or eating patterns. If you know, for example, that skipping meals is a trigger, always keep something in your pocket or purse for munching such as nuts, dried fruit, or a hardboiled egg. Keep a notebook to try to determine your triggers and then avoid them! When that fails, treatments can vary, but most people find relief from triptans such as Zomig or Imitrex.
Continue to Page 4