- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
Can Omega-3s Fight Depression And Build A Stronger Brain?
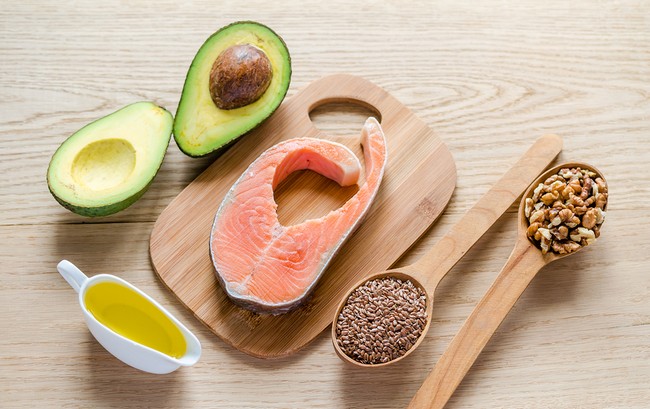

Photo credit: bigstock.com
You’ve probably heard the expression “fish is brain food,” but what does that mean?
Fish, like certain other foods we’ll be discussing in this article, is often rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Among other things, omega-3s play a role in improving brain health and overall cognitive function. Unfortunately, people in industrialized countries are often deficient in omega-3 fats relative to other types of fat. This is, in part, due to the demonization of all forms of fat in the media for the past 50 years. The public is beginning to wake up to the benefits these amazing compounds have for improving overall health, and helping those with neurological conditions like depression. Let’s explore the role of omega-3s in more detail now…
The Lowdown on Omega-3s
There are different types of fatty acids which are found in food. Among these are the three different types of omega fats, omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9, which are classified as polyunsaturated, which means that they will remain liquid at both room and freezing temperatures. Omega fats are considered healthy, but they must be consumed in the proper ratios or certain health problems become more likely. The average American diet, for example, has a highly imbalanced of omega-6s to omega 3s, ranging from 10:1 to 25:1. Researchers have suggested our hunter-gatherer ancestors ate a diet that was much more balanced, with an approximate 1:1 ratio.
At the turn of the 20th century, the use of vegetable oils like canola and safflower oil began to increase dramatically, and the cattle industry began using more grain-based feed. These changes led to the drastic increase in omega-6 consumption, and along with it, a rise in heart disease, cancer and inflammatory conditions.
Omega-3s are an essential fatty acid and cannot be synthesized by the body. The only way to get them is through the diet. The solution to the modern omega fats dilemma is to make sure you are eating the right things (more on that later).
The most important varieties of omega 3s are as follows:
- ALA (alpha linolenic-acid), found mainly in plants
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid)
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
These last 2 forms of omega-3 fats are found primarily in animal protein sources like fish.
Continue to Page 2