- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
This One Melon Can Kill Cancer and Help Diabetics
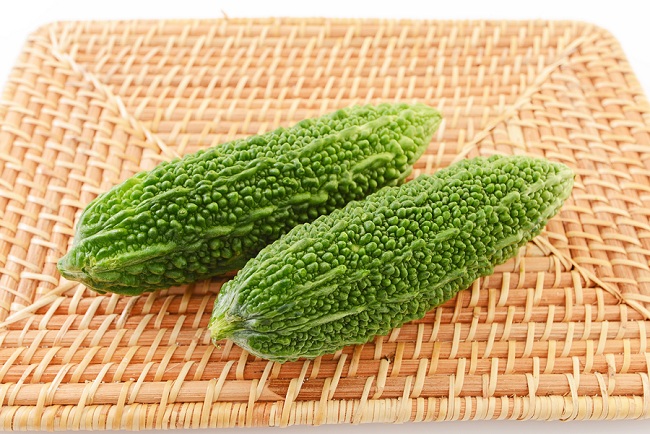

Photo credit: bigstock.com
There is a type of melon, common in other parts of the world, but not well known in America, that has been shown in several studies to kill pancreatic cancer cells, reverse diabetes, and help with other illnesses and diseases. Which melon has such amazing properties? Bitter melon.
Bitter melon is a fruit that grows freely throughout Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean. It’s been used traditionally to treat fever, burns, skin problems, menstruation problems, colic, and chronic cough. This fruit has been used for centuries in Traditional Chinese medicine with no reported or known side effects or problems.
Bitter melon (momordica charantia) goes by several other names: bitter squash, bitter gourd, balsam apple, balsam pear, goya in Japan, ampalaya in the Philippines, and karavel in India. It’s a perennial vine that grows easily in hot, humid climates and has a long, cucumber shaped fruit that has a wrinkled skin that does not look at all appetizing, As the name implies, it’s quite bitter. The flesh is crunch and watery, something like a cucumber or chayote. This is one of the few fruits you will see people eating green as once it turns yellow, it only becomes more bitter the more ripe it becomes. Even the young leaves and shoots from the vine are often used as vegetables in some countries. Most countries put bitter melon in soups or stews or cooked in coconut milk to help hide its bitter flavor.
In Japan, it’s used in place of hops as a bittering agent for beer. It plays an important part in the cuisine of Okinawa and it’s often said that regular consumption of this melon is the reason why most Okinawans live longer than the rest of the Japanese people.
Bitter melon does have an impressive history of medicinal use. It contains anti-bacterial, antiviral, anti-fungal, and anti-inflammatory compounds, which makes it perfect for treating ringworm, gout pain, measles, and skin problems like psoriasis.
However, more importantly than its traditional uses is the exciting research that shows that bitter melon juice can stop diabetes and kill cancer cells in the pancreas. Take a look at what the studies show for both diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
Continue to Page 2

Photo credit: bigstock.com
Cancer of the Pancreas
Pancreatic cancer is a killer and is often difficult to treat, as is rarely discovered until it very late. Traditional means of surgery, radiation, or chemo show very little results.
Almost all tumors have insulin receptors, which move glucose to the cancerous cells so that they can divide and grow. Insulin encourages cancer cells in the pancreas to grow in a dose dependent manner. Since bitter melon regulates insulin levels, this mean it can help prevent the growth of these cells over time.
Researchers at Colorado University looked at the effect that bitter melon had on 4 different lines of pancreatic cancer cells both in mice and in vitro. Mice were randomly divided into two groups, one would receive only water (the control group), while the other set were given bitter melon juice for six weeks. All mice were injected with pancreatic tumor cells.
At the end of the study, researchers found that the mice that were given bitter melon juice had arrested the cancer cell proliferation and induced programmed cancer cell death (apoptosis). In fact, tumor growth was arrested by an incredible 60 percent, when compared to the control group. There was no evidence of negative effects or toxicity within the body.
SEE ALSO: Top 20 Anti-Cancer Herbs and Plants
Researchers from St. Louis University found that extract from bitter melon was also capable of killing breast cancer cells and stopping them from growing or spreading to other parts of the body. Since many people in Asia eat this melon or drink its juice, it’s not surprising that they have much lower rates of cancer. Studies performed in Manila, in the Philippines, show that bitter melon extracts have these types of positive effects on not only breast cancer, but prostate cancer, leukemia, and even HIV (AIDS).
Continue to Page 3
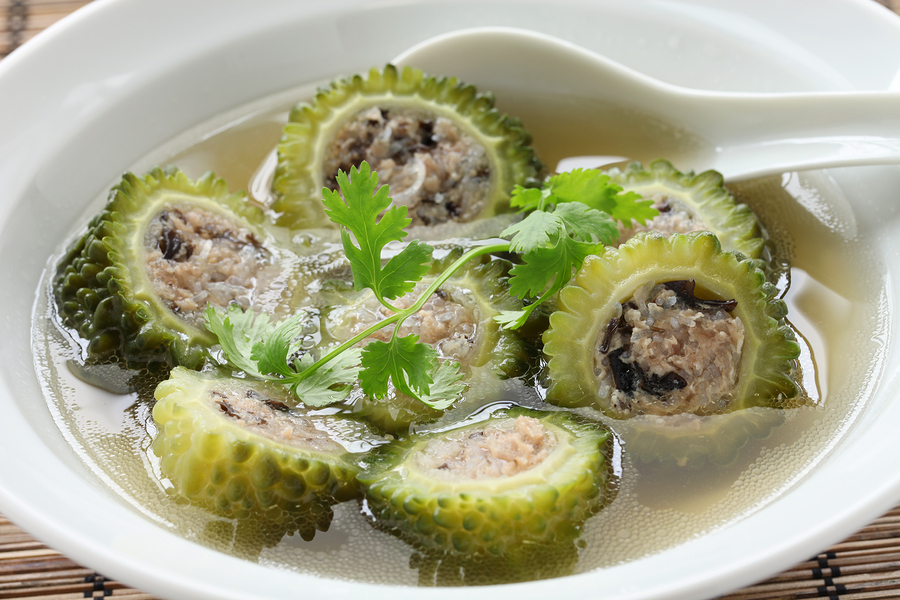

Photo credit: bigstock.com
Diabetes
Several clinical studies have been performed in an attempt to evaluate the ability of bitter melon to control diabetes. Many scientists believe that diabetes can be a precursor for pancreatic cancer so it stands to reason that if bitter melon can stop pancreatic cancer, perhaps it could help with diabetes as well.
In one 4 week study performed in 2011 and published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, showed that in clinical trials, bitter melon had modest hypoglycemic effects for those taking about 2,000mg of bitter melon each day.
There is evidence that shows that this melon can not only increase the number of cells that will go on to produce insulin, but stimulated the production of insulin. Bitter melon might be able to reduce the amount of insulin injections needed, or the amount of medication needed for those with type 2 diabetes.
The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center states that this melon increases the uptake of glucose and stimulates the liver, muscle, and fatty tissue of the body to convert glucose into glycogen, its storage form. These types of changes can reduce overall blood sugar levels and help to lessen the demand on the pancreas.
The international journal Chemistry and Biology published a study in 2008 that showed that bitter melon improved glycemic control and helped cells uptake glucose. It also showed an overall improved tolerance to glucose. Mice were used in this study and it has lead scientists to believe that bitter melon hold a great deal of promise in the treatment of diabetes.
Bitter melon is a great source of vitamins as well, including vitamin B, C, and A. It also contains important minerals such as iron, potassium, calcium, and offers the body fiber. It has twice the calcium of spinach, twice the potassium of a banana, and twice the beta-carotene of broccoli. Find out other calcium sources.
You can find fresh bitter melons at most Asian stores located in America, and the juice, tea, and extracts are generally found either online or in local health food stores.
If you would like to try the fresh fruit, the best way to get rid of the bitterness is to soak the sliced up fruit in some salt water for 30 or 40 minutes before cooking or eating. If you want to make fresh juice from it, mix with other sweet juices, such as apples or grapes, and/or add a touch of honey.
An important note: Don’t consume more than 2 ounces of this melon in a day (this would be about 2 whole melons) as it can cause diarrhea and upset stomach for some people. Also, if you are pregnant, you should consume very little or wait until after you have given birth as eating too much of this melon can cause bleeding and contractions.
If you are a diabetic, talk to your doctor before stopping any medications. Ask them about consuming bitter melon to ensure that there are no drug interactions.
References: