- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
How Did Something This Tiny Become One Of The World’s Most Efficient Killers
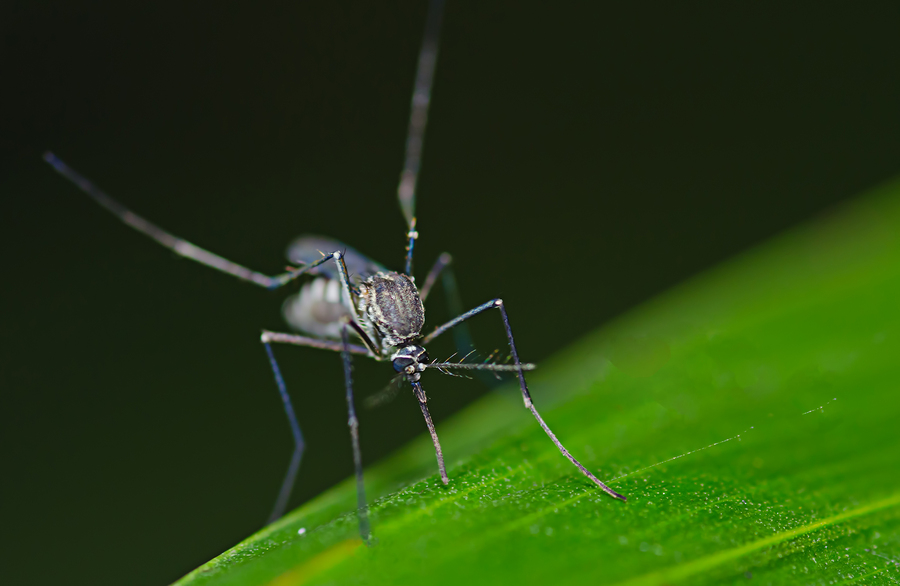

Photo credit: bigstock.com
Now, many species of mosquitoes have developed a resistance to many insecticides. The Aedes Aegypti is back with a vengeance! And with it, many diseases such as dengue fever. There is now a vaccine for yellow fever, but not dengue fever or Zika.
When you think about it, this means that we have been trying to kill off these little disease spreading plague for almost one hundred years! The mosquitoes have learned and adapted. Have humans?
We are trying. The World Health Organization has encouraged countries hit hardest with Zika and dengue to try genetically engineered mosquitoes to help curb the massive problem of Aedes Aegypti mosquito.
Yes, there are other types of mosquitoes that spread disease but most of them are under at least partial control. As dengue fever and Zika continues to spread throughout the Americas, and is now being found in other countries, health authorities are asking themselves, how do we fight back before this mosquito comes to our country, and how do we fight it where it lives now?
It is possible. Not cheap and not easy, but possible. Many feel that the best way to dramatically decrease the population is to release genetically modified (GM) mosquitoes. These will breed with wild mosquitoes, but their offspring are sterile. This means that just one generation later, the mosquitoes die off and leave no offspring behind. By using GM mosquitoes, you remove the dangers of using toxic poisons. Another option is to introduce male mosquitoes which carry the Wolbachia bacteria. This type of bacteria is found in about 60 percent of all insects and does not affect mammals, only insects. When infected, male mosquitoes breed with females and the resulting eggs are infertile.
READ ALSO: This One Natural Oil Is Just As Effective At Repelling Mosquitoes As DEET
Although mosquitoes are perhaps one of the earth’s tiniest and insignificant creatures, it still remains a fact that they can wreak havoc on millions of human lives.
References: