- Make It Yourself Lavender Heart-Shaped Bath Bombs!
- 20 Things You Never Knew About “Down There”
- 12 Best Foods For Those Suffering From Arthritis Pain
- 12 Personal Hygiene Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes (Mom Never Told You About #4!)
- 15 Medicinal Plants And Herbs From The Cherokee People
- 12 Mind-Blowing Benefits Of Drinking Coconut Water During Pregnancy
- 12 Outstanding Winter Foods That Won’t Fatten You Up Like A Christmas Turkey
Turmeric Promotes All-Round Health
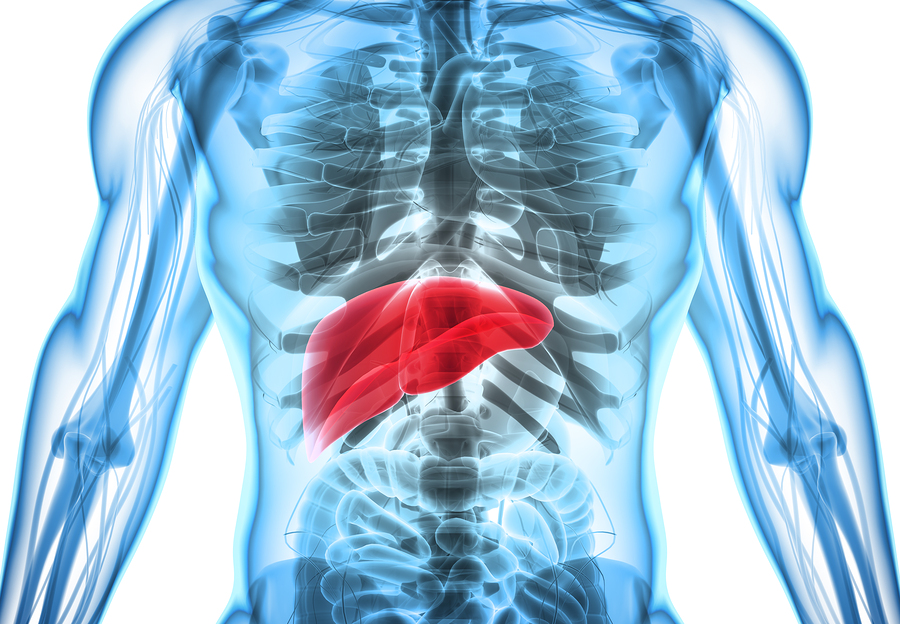
10. Liver health
Curcumin has long been associated with liver health. The anti-inflammatories help to prevent liver damage, while the high antioxidant content of the compound keeps the free radicals from attacking the liver. The liver is also protected from heavy metal toxins such as mercury and lead, which are taken in from the environment.
Adding curcumin to your diet through turmeric is fairly simple, as the spice can be added to food, especially curries, casseroles, and stews. However, it is unlikely to give you the therapeutic dose you need. The best way to go is via natural, curcumin or turmeric supplements, or even a complex supplement of the two.
The results of the studies have resulted in some pharmaceutical companies looking into the merits of producing a synthetic form of curcumin supplements. Natural health practitioners agree that synthetic curcumin may not have the same effects as the all-natural products, and could potentially have some side-effects.
When taken in normal doses there are no side-effects except a possible mild skin reaction in the form of an itchy rash. However, there are some precautions to note.
- Supplements should be avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding because there is no documented research on curcumin for children.
- Those on blood-thinning meds should not take the supplements, although a small amount of the spice can be added to food.
- Because of the anti-coagulant properties, supplements should be discontinued about 2 weeks before planned surgery.
- If you are on any medication, allow a gap of 3 to 4 hours before taking your daily curcumin supplement.
READ ALSO: Turmeric & Its Anti-Inflammatory Qualities Infographic
Ancient eastern civilisations used Turmeric over the centuries as a spice and medicinal herb, and many even considered it a magic potion!
Modern research has now proved that turmeric is not magic – but a true miracle herb.
References: